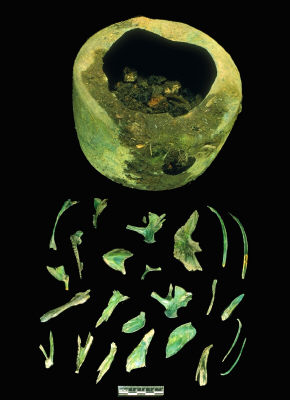
Wooden and brass pipe representing Kan Lituya in the form of a Supernatural Frog, and his Bear Slave creating waves in Lituya Bay. Source: de Laguna, Volume. 3
My recent post on the 1786 visit by La Perouse to Tsunami-prone Lituya Bay, Alaska sent me scurrying to download the massive ethnography by Frederica de Laguna entitled Under Mount St. Elia Under Mount Saint Elias: The History and Culture of the Yakutat Tlingit. As expected, there is a rich oral history of waves in this bay. From Volume 1, page 94, she says
Emmons (1911, p. 295) recorded Indian beliefs about the dangers of Lituya Bay, caused by:
“… a monster of the deep who dwells in the ocean caverns near the entrance. He is known as Kan Lituya, ‘the Man of Lituya’ [qa htu ‘a?]. He resents any approach to his domain, and all of those whom he destroys become his slaves, and take the form of bears, and from their watch towers on the lofty mountains of the Mt Fairweather range they herald the approach of canoes, and with their master they grasp the surface water and shake it as if it were a sheet, causing tidal waves to rise and engulf the unwary.
De Laguna then continues to discuss an extraordinary wooden smoking pipe, illustrated above:
“This legend of Lituya is illustrated by a carved wooden pipe (fig. 50) [pi. 123], of splendid proportions, which was obtained in 1888 from the chief of the Tuck-tane-ton family of the Hoon-ah Kow [DAqdentan sib of Hoonah], who claimed this bay as his hereditary sea-otter hunting ground. It was used only upon occasions of particular ceremony—when the clan assembled to honor the dead, or to deliberate upon some important question of policy. At one end is shown a froglike figure with eyes of haliotis shell, which represents the Spirit of Lituya [possibly the Frog crest of the sib?], at the other end the bear slave sitting up on his haunches. Between them they hold the entrance of the bay, and the two brass-covered ridges are the tidal waves they have raised, underneath which, cut out of brass, is a canoe with two occupants, that has been engulfed. [Author’s note: This illustration was furnished through the courtesy of Mr George G. Heye, in whose collection the pipe now is.”]
One thng leading to another, I thought I would look into whether the Tlingit story of La Perouse’s visit had been passed on. As it turns out, the early ethnographer G.T. Emmons records an account given by a Tlingit chief one hundred years after the visit of La Perouse to Lituya Bay. This gives an indigenous perspective on what must have been an extraordinary series of events for both parties. This account is well worth reading, so I am reproducing a portion of Emmons (1911) rendering below:
“In 1886, one hundred years after [the vist of la Perouse], Cowee, the principal chief of the Auk qwan of the Tlingit people, living at Sinta-ka- heenee, on Gastineaux Channel, told me the story of the first meeting of his ancestors with the white man, in Lituya Bay, where two boats of the strangers were upset and many of them were drowned. This narrative had been handed down by word of mouth for a century. These people possess no records nor had the chief, who spoke no word of our tongue, ever heard of La Perouse from outside sources; so we can here authenticate by an exact date a most interesting piece of native history in detail, the truth of which is substantiated by the fact that La Perouse was the only one of the early navigators to visit this locality in a large ship and by the attending loss of life in the destruction of his two boats. Continue reading →