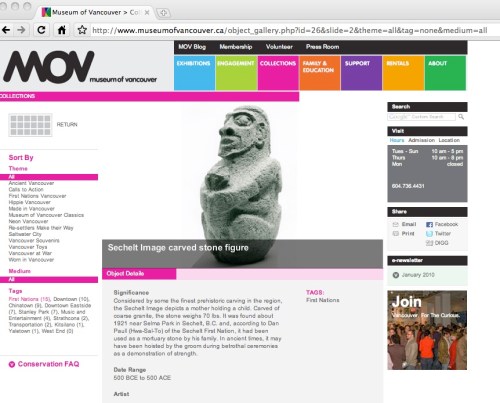
The Sechelt Image. Detail of Screenshot from the Museum of Vancouver. (click for full screen or scroll down)
The Museum of Vancouver has a pretty slick and punchy website from a design point of view, very “Web 2.0” with bright colours and links to twitter and facebook and the like. But in some respects it fails, and fails badly. Consider the image above: the “Sechelt Image”, a stone sculpture and one of the most famous objects in BC Archaeology. A single low-resolution picture is offered, a link to which is not possible, and downloads of which are deliberately made difficult. And in this protective bubble, the object can only be seen as a pale, grainy image, surrounded by the Museum’s loud and crass colour scheme. (Update: see full screenshot below: the Vancouver Museum overlays its neon social web over the Sculpture much like Vancouver itself overlays aboriginal culture).
Fine – I am used to that ridiculous phenomenon wherein Public Institutions think they own the images that they are entrusted with – if the image is allowed to be seen by the descendent communities (and in this case I wonder if it really is) then why can it not be seen in high resolution, free from the magenta borders and the exhortations to tweet!?
But the real problem is that the web designers, with their stupid and un-necessary banner reading “Sechelt Image carved stone figure”, obscure an important area of the sculpture, including the all-important vulva which reveals, as noted by Wilson Duff, that this sculpture is powerfully hermaphroditic. It is not just bad and regressive museology to cover up an important part of an object, but I believe it is deeply disrespectful as well. By obscuring part of the image and by imprisoning it within their branded frame and obfuscating web design, they, the (hopefully) temporary guardians of this powerful piece of art, are visually co-opting it for what amounts to advertising purposes. There is no reason to put your label over top of that which you claim to be displaying for its own sake; no reason other than marketing zeal and lack of control over the web designers.
You might think it was just prurience over the frankly sexual image, but below we see another image from their website with no shocking! vulva! to conceal, which has been similarly branded and bounded by the MoV. Maybe I am just mad at them still because they’re using a petroglyph boulder as a rock garden (note the obscuring “petroglyph” banner) but really: their website is an egregious example of stealth appropriation and blatant disrespect under the disguise of progressive design and social networking. And I’m just a dumb archaeologist: I’d love to see a Visual Anthropologist dissect the public face they are so eager for the world to see, the face they insist must frame every image on their website.