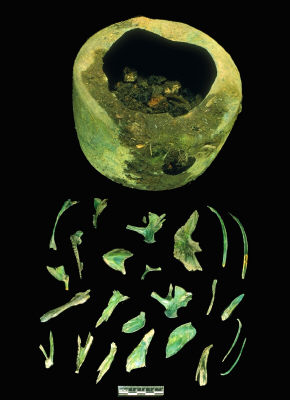
I was feeling sick yesterday and this picture didn’t help: from the Castle Hill excavations at Sitka, Alaska (previously 1, 2) is the nearly complete copper kettle. Inside, the archaeologists found the green-stained bones from the heads of three codfish (true cods, Gadidae, are 35% of the fish assemblage). One of the great things about archaeology is to get these tiny slices of life: someone’s kettle of fish, set aside one day 200 years ago.
At a bigger scale, archaeology isn’t always so straightforward though. Interestingly, from the site as a whole, only 1% of the fish bones are from halibut (11 bones in total). This is despite the fact that:
Cod dominated the Castle Hill assemblage, and yet, Emmons (1991:148) stated that cod was considered an unimportant part of the Tlingit diet if salmon and halibut were available. Historic records confirm that cod was popular in Sitka, because it was available almost year around (Gibson 1976:40, Khlebnikov 1994). Halibut was also popular because of its year around availability and was sold to the Russians in large numbers. Between 22,000 and 138,000 pounds of halibut were purchased each year from the Tlingit from 1846 to 1866 in addition to the yearly average of 13,000 pounds of halibut the company procured itself (Gibson 1987:94). The emphasis on halibut brought to Sitka and sold to the Russian-American Company would lead to the prediction that halibut should dominate the assemblage, yet this is not the case. It may be a case where cod were readily available and not worthy of special consideration in historic documents.
Two things strike me about this. One is that the Tlingit, using largely traditional methods at the time, were able to produce up to 138,000 pounds of excess halibut for trading purposes. That’s a lot of fish. The other is that so much halibut renders down to so few bones. Halibut is long known on the NW Coast as being strongly under-represented in archaeological sites, probably because it may have been butchered on the beach and the bones, which separate cleanly from the meat, would end up in the intertidal zone and be washed away or eaten by dogs. It also seems possible that the Tlingit were trading in dried, boneless halibut (which makes the tonnage involved all the more impressive). And certainly the entire site was not excavated, so there may be a mother lode of halibut bones somewhere. But this case makes an interesting cautionary tale in zooarchaeology: we seldom have an accurate sense of the scale of the incoming fish quantities to compare to what is left in the ground, and when we do, the degree of difference between the written and material records is often quite startling!

Tlingit women and children cleaning fish on the beach, ca. 1907. Ignore the racist caption. Source: U. Washington.